Blockchain is changing how businesses manage trade credit, making processes faster, cheaper, and more secure. Here’s how:
- Smart Contracts: Automate payments and approvals, reducing delays and cutting costs by up to 70%.
- Tokenization: Turns invoices and receivables into digital assets, providing instant liquidity.
- Stablecoins & CBDCs: Enable near-instant, low-cost cross-border payments, bypassing traditional banking systems.
- Fraud Reduction: Blockchain’s tamper-proof records cut fraud rates from 1% to 0.1%.
- Efficiency Gains: Processing times drop from over 8 days to just hours, with costs reduced by 93%.
These advancements are helping businesses – especially SMEs – access financing, improve cash flow, and reduce risks. However, challenges like inconsistent regulations and the need for legal recognition of digital documents remain. Combining blockchain with tools like accounts receivable insurance can provide extra security as companies navigate this evolving landscape.
Why Blockchain is FINALLY Changing Trade Finance
sbb-itb-2d170b0
How Blockchain Improves Trade Credit Processes
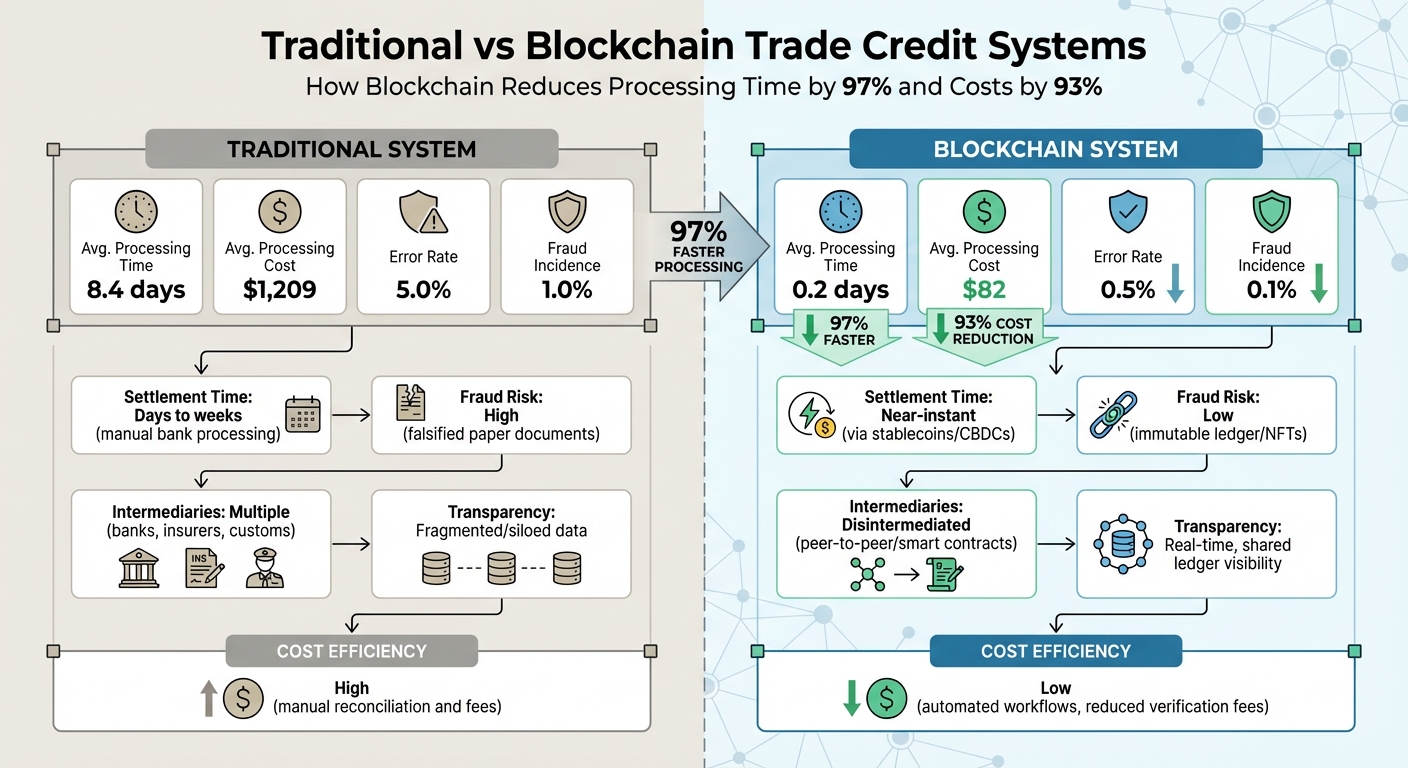
Traditional vs Blockchain Trade Credit: Processing Time, Cost, and Risk Comparison
Blockchain introduces a shared, real-time digital ledger to streamline U.S. trade credit processes. This unified approach eliminates the fragmented recordkeeping seen in traditional trade finance, where exporters, importers, banks, and customs agencies each maintain separate systems. The results? Processing times drop dramatically – from 8.4 days to just 0.2 days – and transaction costs shrink from $1,209 to $82. Let’s break down how blockchain achieves these efficiencies, focusing on transparency, automation, and fraud prevention.
Transparent and Permanent Records
Blockchain creates a tamper-proof, shared ledger that acts as a "single source of truth" for all trade credit transactions. Authorized participants can access permanent, unaltered records of invoices, letters of credit, and shipping documents. This level of transparency ensures everyone is on the same page, reducing disputes and delays. For example, platforms like those used by Dubai Customs and Maersk/IBM have significantly reduced clearance times.
At the same time, blockchain balances transparency with privacy. Tools like Zero-Knowledge Proofs enable parties to verify key details – such as payment capability or creditworthiness – without revealing sensitive data. This means businesses can maintain confidentiality while still benefiting from the system’s openness.
Smart Contracts for Automated Workflows
Blockchain doesn’t just store data – it also powers automation through smart contracts. These self-executing contracts automatically trigger payments or other actions once specific conditions, like delivery confirmation, are met. This eliminates the need for manual approvals and third-party checks, cutting trade settlement costs by up to 70% and improving cash flow for suppliers.
"The advent of smart contracts is critically important to its adoption for trade finance – without it, we would not be able to model the functionality and provisions of a letter of credit or bill of lading." – Josias N. Dewey, Partner, Holland & Knight
Additionally, smart contracts can integrate real-time compliance checks for Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations. For small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), this means faster settlements – often reducing timelines from weeks to mere minutes – freeing up liquidity and improving access to working capital.
Fraud and Risk Reduction
Blockchain’s immutable records tackle one of trade finance’s biggest vulnerabilities: fraud. By ensuring that invoices or warehouse receipts can’t be used as collateral for multiple loans, blockchain mitigates risks like the infamous 2014 Qingdao Metals Fraud, which resulted in $3 billion in losses. In controlled tests, fraud rates dropped from 1.0% to 0.1%, while errors in trade documentation decreased from 5% to just 0.5%.
Here’s how the numbers compare:
| Metric | Traditional System | Blockchain System |
|---|---|---|
| Avg. Processing Time | 8.4 days | 0.2 days |
| Avg. Processing Cost | $1,209 | $82 |
| Error Rate | 5.0% | 0.5% |
| Fraud Incidence | 1.0% | 0.1% |
Blockchain’s benefits don’t stop there. With the help of IoT sensors, businesses can continuously monitor collateral in real time, ensuring goods exist and remain in acceptable condition throughout the transaction. This added layer of oversight further strengthens trust and reduces risk in trade credit processes.
Fintech Solutions for Trade Credit Access
Traditional banks reject nearly half of trade finance applications, leaving small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) – which contribute 60% to global GDP but receive less than 3% of available credit – at a disadvantage. Blockchain-based fintech platforms are changing the game, leveraging alternative data, AI-powered credit assessments, and direct global market access. These innovations eliminate the delays and red tape that have historically kept smaller businesses from thriving in international trade. Let’s dive into how these tools are reshaping trade credit.
Alternative Data for Credit Assessment
Fintech platforms are moving beyond traditional credit scores to assess creditworthiness. They now consider real-time transaction data, supply chain performance, and trade volumes. This shift is a lifeline for businesses with limited credit histories but solid operational performance. Blockchain technology plays a key role here, creating a tamper-proof record of transactions, shipments, and payments. This transparency gives lenders a full picture of a company’s reliability without needing manual reconciliation or third-party verification.
Take Komgo, for instance. This platform has streamlined Know Your Customer (KYC) processes, allowing smaller businesses to verify digital documents and transaction histories in just hours instead of weeks. By combining data sources, fintech firms can also offer services like invoice factoring, where exporters can receive up to 90% of an invoice’s value within 24 hours – an invaluable solution for businesses dealing with long international payment cycles.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
AI tools integrated with blockchain platforms are revolutionizing risk assessment. These systems analyze patterns across thousands of transactions, identifying anomalies and evaluating risk in real time. This replaces the cumbersome, paper-heavy processes that burden 32% of small manufacturers and 46% of small service firms. For example, XinFin XDC uses AI alongside blockchain to automate trade finance agreements and continuously monitor credit risks, adjusting terms dynamically as market conditions evolve.
In April 2025, Standard Chartered’s SC Ventures collaborated with fintech SWIAT and digital platform Olea to enable supplier financing through blockchain. This partnership resulted in a tokenized receivable funded by DekaBank, illustrating how AI-driven platforms can automatically connect creditworthy suppliers with institutional lenders. By 2025, blockchain-based accounts receivable financing is expected to reach 3.6 trillion yuan, reflecting the rapid adoption of these AI-enhanced tools. These advancements are laying the groundwork for broader market access, as we’ll see next.
Global Market Access for SMBs
Blockchain technology is eliminating intermediaries, cutting transaction times from weeks to real time, and drastically reducing costs. High-performance networks like Polygon, which can process 65,000 transactions per second compared to Ethereum’s 17, make small-scale international trade feasible with transaction fees under a penny.
In July 2023, the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) successfully tested a project with central banks from China, Hong Kong, Thailand, and the UAE. This trial facilitated over 160 cross-border payments and foreign exchange transactions, moving more than $22 million using interoperable Central Bank Digital Currencies (mCBDCs).
"Global trade is no longer reserved for giants. With the right financing tools, even the smallest shop can ship worldwide and get paid without stress." – Amash Hayat, Author, Global Trade Magazine
Platforms like TradeIX Marco Polo and Contour simplify international trade for SMBs by offering pre-verified networks that ease KYC and regulatory compliance. Smart contracts further streamline operations by automating Letters of Credit and releasing funds instantly once IoT sensors or digital records confirm shipping conditions. These tools address cash flow challenges, making international trade less risky and more accessible for smaller businesses.
For added security, businesses can explore specialized solutions like Accounts Receivable Insurance (https://accountsreceivableinsurance.net), which offers tailored strategies to protect against payment defaults and other financial risks. By combining blockchain’s efficiency with advanced risk management tools, these solutions are transforming how SMEs navigate global trade.
Tokenization and Instant Settlement
Tokenization turns trade credit assets into digital tokens, allowing them to be traded, divided, and settled instantly. This process replaces the traditional 30–90-day payment cycles that often tie up liquidity. By converting invoices, letters of credit, and receivables into blockchain-based tokens, businesses can unlock immediate liquidity rather than waiting for long settlement periods.
Tokenization of Trade Credit Assets
Imagine a $100,000 invoice being tokenized into 100 units of $1,000 each. This fractional approach allows smaller investors to participate in trade finance, giving businesses access to a wider range of funding options. Instead of enduring lengthy approval processes for financing, companies can tap into a more diverse capital pool through transparent secondary markets.
In October 2023, Citi introduced its "Citi Token Services for Cash" program, leveraging distributed ledger technology and smart contracts to offer institutional clients tokenized deposits and automated trade finance solutions available around the clock.
"By using distributed ledger technology and smart contracts, Citi has created a patented programmable payment and liquidity platform, which will reduce costs and streamline processes." – Citi
Once a delivery is confirmed through digital verification tools like IoT sensors, payments are automatically released to suppliers. What used to take weeks now happens within hours. Additionally, businesses can trade tokenized assets on secondary markets even before the underlying transaction matures. This innovation in liquidity management also extends to cross-border transactions, where blockchain simplifies payments even further.
Blockchain-Powered Cross-Border Payments
Beyond improving liquidity, blockchain is transforming cross-border payments by cutting out intermediaries. Traditional international transactions rely on a network of correspondent banks, which often introduce delays and extra fees. Blockchain, with its unified ledger operating 24/7, eliminates these intermediaries. It enables atomic settlement, where the transfer of goods and payment occur simultaneously on-chain, reducing counterparty risk and timing mismatches.
In July 2025, Kinexys by J.P. Morgan, Ondo Finance, and Chainlink successfully completed a cross-chain Delivery versus Payment (DvP) transaction using the Chainlink Runtime Environment. This proved that instant settlement across different blockchain networks is technically possible. Banks are also adopting methods that convert local currency into a stablecoin, transfer it instantly via blockchain, and then convert it back to domestic currency.
The potential savings are enormous. Tokenized payment infrastructure is expected to reduce the cost of corporate cross-border transactions by 12.5%, potentially saving businesses over $50 billion by 2030. With the global trade finance gap hitting $2.5 trillion in 2023 – a 50% increase from 2020 – such efficiencies are crucial to keeping global trade flowing.
"The efficiencies gained by advancements in tokenized payment infrastructure should lower the cost of corporate cross-border transactions by 12.5%, which would save business customers over US$50 billion by 2030." – Deloitte
For businesses handling international receivables, combining blockchain’s instant settlement capabilities with tools like Accounts Receivable Insurance creates a solid risk management strategy. While blockchain ensures faster and more transparent payments, specialized insurance protects against financial risks that can still arise in cross-border trade. Together, tokenized assets and instant settlement offer a powerful way to enhance trade credit efficiency while managing risks effectively.
Regulatory and Standardization Challenges
Blockchain’s growth faces hurdles tied to both regulatory and technical factors. One major issue is the lack of consistent regulations across different regions, which complicates compliance – especially for stablecoins used in cross-border transactions. Financial institutions are also cautious about using public blockchains due to data privacy concerns. Instead, they often favor permissioned ledgers where participants are identifiable, and sensitive trade details remain confidential.
Another challenge is the legal recognition of digital documents. Traditional trade finance relies heavily on paper-based tools like letters of credit and bills of lading. For blockchain to replace these, legal reforms are essential. An example is the Model Law on Electronic Transferable Records (MLETR), which has already been adopted by countries like the UK, France, and Singapore. These obstacles highlight the need for regulatory and industry collaboration to create standardized solutions.
Standardization Efforts in Blockchain Applications
Efforts to standardize blockchain applications are underway, led by organizations like ITFA, ICC, and DCSA. These groups are working to connect isolated "DLT islands" and address interoperability challenges.
On the technical side, standards like ISO/TR 24332:2025 have been introduced to ensure that records shared across blockchain systems remain both legally and operationally valid. These standards include "inter-chain interoperability components" that ensure transaction consistency. For instance, if a cross-chain transaction fails or times out, it can be automatically reversed across all involved platforms.
In December 2025, a milestone in interoperability was achieved when ICE Digital Trade, GSBN, and IQAX successfully completed the first live cross-platform electronic presentation of documents under an eUCP Letter of Credit. This demonstrated that different digital trade platforms could exchange documents and settle trade finance obligations seamlessly.
Regulatory Progress in 2025
As standardization advances, regulators are also making strides to support blockchain adoption. Central banks are playing a key role, with 127 countries or currency unions exploring CBDCs and over 20 having already launched them by early 2025. For instance, China’s digital yuan has facilitated transactions exceeding $250 billion since its broader launch.
In July 2023, a trial involving Chinese state-owned banks and central banks in Hong Kong, Thailand, and the UAE processed over 160 cross-border payments worth $22 million. This trial showcased the efficiency of real-time CBDC settlements.
Project Mandala is another important development. This initiative, involving the BIS Innovation Hub Singapore Centre and central banks from Australia, Korea, Malaysia, and Singapore, aims to embed jurisdiction-specific regulatory requirements directly into blockchain protocols. By automating compliance for cross-border transactions, the project addresses one of the most time-consuming aspects of international trade finance.
"Regulators are firmly supporting the introduction of new technologies such as digital assets, across both trade financing and payment processing. Recent regulatory developments include EU’s MiCA and UK’s Property Bill whilst the US market will catch up promptly." – André Casterman, Chair of the Fintech Committee, ITFA
For businesses handling international receivables, these regulatory efforts provide clearer guidance. While standardization is still evolving, companies can already take advantage of blockchain’s transparency by pairing it with traditional tools like Accounts Receivable Insurance. This approach helps mitigate non-payment risks that remain, even in a digitized trade landscape.
Business Benefits of Blockchain in Trade Credit
Blockchain tackles some of the biggest inefficiencies in trade credit systems. Traditional methods often involve manual workflows, fragmented data, and numerous intermediaries – all of which increase costs and slow down transactions. Blockchain, on the other hand, offers a shared, tamper-proof ledger that can be accessed in real time, eliminating the constant need for reconciliation and verification.
Operational and Financial Benefits
Shifting from paper-heavy processes to blockchain-based automation brings significant improvements to trade credit management. For example, smart contracts can automatically execute payments once certain conditions are met, reducing settlement times from days – or even weeks – to just a few hours. By removing intermediaries, businesses can cut transaction fees and avoid delays caused by conventional banking processes.
| Feature | Traditional Trade Credit | Blockchain-Based Trade Credit |
|---|---|---|
| Settlement Time | Days to weeks (manual bank processing) | Near-instant (via stablecoins/CBDCs) |
| Fraud Risk | High (falsified paper documents) | Low (immutable ledger/NFTs) |
| Intermediaries | Multiple (banks, insurers, customs) | Disintermediated (peer-to-peer/smart contracts) |
| Transparency | Fragmented/siloed data | Real-time, shared ledger visibility |
| Cost Efficiency | High (manual reconciliation and fees) | Low (automated workflows, reduced verification fees) |
In addition to these operational enhancements, blockchain also reshapes how businesses approach risk management in trade credit.
Credit Risk Management Improvements
Blockchain offers a more dynamic approach to credit risk management by leveraging real-time operational data instead of relying solely on static credit scores. For instance, smart contracts can trigger payments automatically once delivery is confirmed through digital bills of lading. This minimizes the risk of payment delays. The technology’s immutable ledger also prevents invoice fraud and duplicate financing. Additionally, non-fungible tokens (NFTs) provide cryptographic proof of asset authenticity, ensuring counterfeit collateral doesn’t enter the credit system.
"Blockchain can reduce credit examination costs in the trade credit process and share credit risk in the supply chain, leading to financing equilibrium and increased member profit levels." – Lei Yang, IEEE Access
Blockchain also fosters reputational accountability. Transactions recorded on a shared ledger make payment failures visible to all network participants, creating a strong incentive for timely repayment. For businesses managing international receivables, this visibility can be paired with Accounts Receivable Insurance to form a robust risk management strategy that addresses both modern and traditional credit risks.
Another notable feature is the use of zero-knowledge proofs (ZK-proofs), which allow companies to demonstrate compliance with financial covenants without revealing sensitive information. This strikes an important balance between transparency and privacy, especially for businesses involved in complex, multi-party trade arrangements.
Conclusion
Blockchain is transforming how businesses handle trade credit and accounts receivable, offering faster processing times and lower transaction costs. With the blockchain market expected to reach $331.71 billion by 2032, this shift is picking up speed. However, alongside these advancements come challenges that demand careful attention.
While the technology delivers operational improvements, its success hinges on overcoming regulatory hurdles and ensuring data quality. Regulatory frameworks remain inconsistent across regions, and fragmented standardization efforts add complexity. Even the most advanced blockchain systems are only as reliable as the data they process. Businesses that adopt blockchain without addressing these issues risk exposing themselves to vulnerabilities beyond the technology’s scope.
"Trade credit insurance is emerging as a key enabler. It provides businesses with the reassurance they need to thrive in an uncertain economic environment." – Marsh Specialty
The best strategy combines blockchain’s efficiency with robust risk management tools. Accounts Receivable Insurance offers the financial security needed to pursue growth opportunities while adopting innovative fintech solutions. This approach allows businesses to confidently extend competitive credit terms, explore new markets, and utilize tokenized assets – all with protection against counterparty risks and regulatory uncertainties.
As blockchain evolves through 2025 and beyond, companies that strategically integrate the technology – balancing innovation with risk management – will be well-positioned to seize the $16.1 trillion tokenization opportunity forecasted by 2030. The focus isn’t just on adopting blockchain but on preparing thoughtfully for its integration. This balanced approach reflects a broader trend in trade finance where innovation works hand in hand with risk mitigation.
FAQs
What trade credit tasks should be prioritized for blockchain?
Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize accounts receivable by automating and digitizing core tasks. It can simplify processes like transaction verification, minimize fraud risks, and boost transparency. Key applications include payment processing, smart contract execution, and record-keeping.
In cross-border trade finance, blockchain shines by cutting processing times from days to just hours. This not only lowers costs but also improves liquidity management and speeds up transaction settlements, making financial operations more efficient and streamlined.
How do tokenized invoices work in real-world financing?
Tokenized invoices turn outstanding invoices into digital tokens stored on a blockchain. These tokens, generated through smart contracts, simplify processes like verification, transfer, and settlement, cutting down on paperwork while making transactions more transparent. For businesses, this means quicker access to cash. By selling these tokens, companies can secure liquidity without relying on traditional lending methods. This system is especially helpful for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), as it improves cash flow, ensures secure transactions, and opens up trade finance opportunities through fractional ownership.
What legal and compliance hurdles could delay adoption in 2025?
Legal and compliance hurdles could potentially slow down the adoption of blockchain in trade credit by 2025. One major factor is the evolving legal framework surrounding digital assets. For instance, updates to the Uniform Commercial Code (UCC), particularly Article 12, focus on addressing controllable electronic records. These updates aim to provide clarity but may require time for widespread implementation and understanding.
Another challenge lies in adapting existing regulations to emerging technologies like virtual currencies and distributed ledger systems. Ensuring compliance with anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements adds another layer of complexity. These regulations are essential for creating secure and trustworthy ecosystems, but navigating them could lead to delays in blockchain’s broader adoption in this space.



