AI is changing how trade credit insurance works, making it faster and more reliable. Here’s the key takeaway: insurers now use AI to analyze real-time data, predict risks months in advance, and detect fraud with unmatched precision. This helps businesses protect cash flow and avoid losses caused by nonpayment.
Key points:
- Real-time risk analysis: AI processes data like news, transactions, and supply chain updates instantly.
- Fraud detection: Algorithms spot suspicious patterns that humans might miss.
- Faster claims processing: Automation reduces delays and improves accuracy.
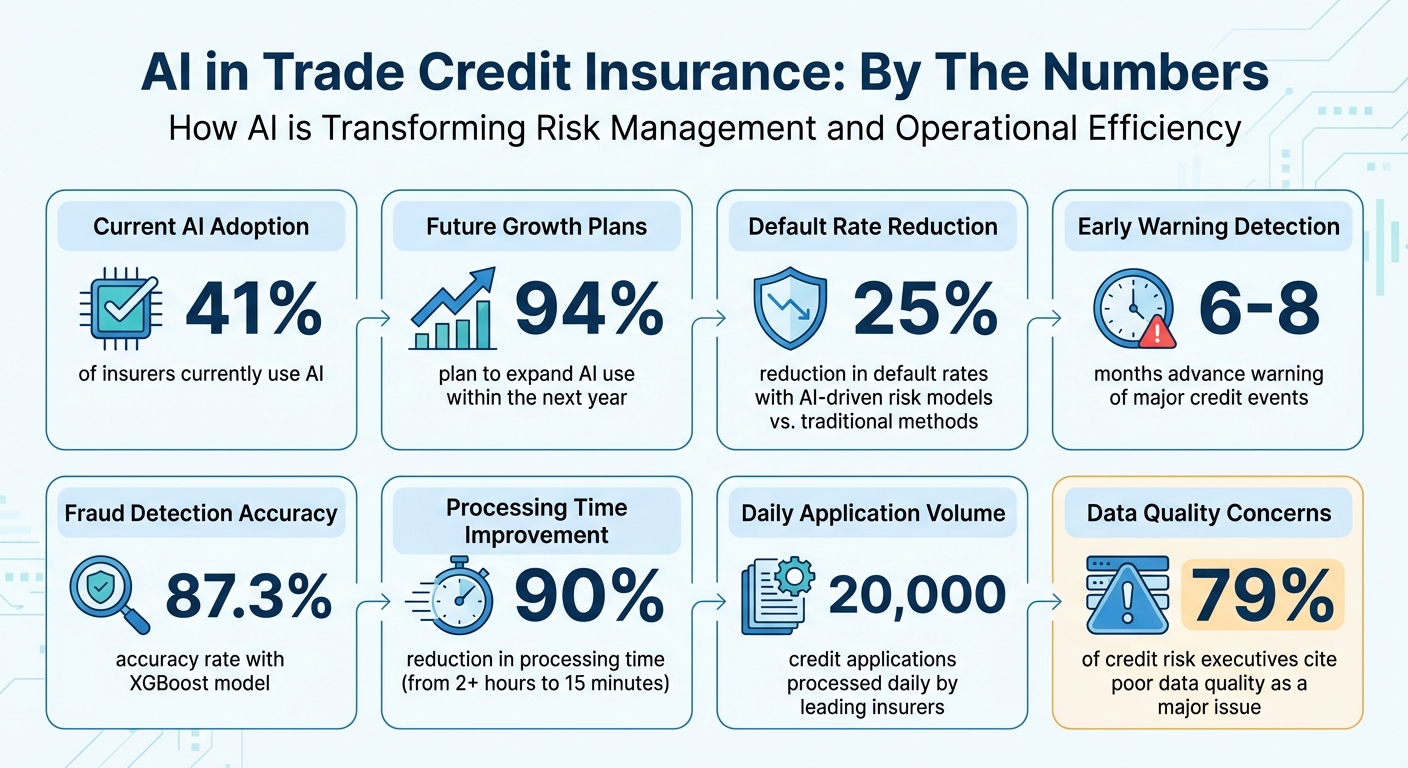
- Industry adoption: 41% of insurers already use AI, and 94% plan to expand its use.
AI-powered systems are transforming credit assessments, fraud detection, and claims handling, enabling insurers to handle large volumes efficiently while maintaining human oversight. The future of trade credit insurance lies in combining AI with strong data governance, secure systems, and trained teams.
AI Adoption and Impact in Trade Credit Insurance: Key Statistics
TCI Week 2023 – Artificial Intelligence in Trade Credit Insurance
sbb-itb-2d170b0
Challenges in Trade Credit Insurance Risk Management
Trade credit insurance plays a crucial role in protecting businesses, but insurers face several obstacles that hinder their ability to manage risks effectively. These challenges include outdated evaluation methods, limited access to essential financial data, and reliance on labor-intensive manual processes that struggle to keep up with modern business demands.
Inaccurate Credit Assessments
Traditional credit assessments often fall short because they rely on historical financial data that may not accurately reflect a company’s current financial standing. For instance, underwriters typically base decisions on quarterly reports, which may already be outdated by the time they’re reviewed. This lag leaves insurers vulnerable to sudden changes in a buyer’s financial health.
The issue is even more pronounced when dealing with privately held companies. Unlike publicly traded firms, private businesses don’t disclose their financial details as openly, making it challenging to access critical information like cash flow or emerging financial stress. Without real-time insights, even seasoned underwriters find it difficult to evaluate creditworthiness accurately.
The stakes are high. Studies show that AI-driven risk models can reduce default rates by as much as 25% compared to traditional methods. André Düsing, Senior Manager Corporate Strategy at Atradius, highlights the potential of AI in this area:
"AI models might also be sensitive to patterns and trends that might be missed by human observers, thus enhancing the precision of risk assessments."
These gaps in credit assessments also weaken defenses against fraud, an issue explored in the next section.
Fraudulent Claims and Limited Visibility
Detecting fraudulent claims remains one of the toughest challenges in trade credit insurance. Traditional statistical methods often fail to identify the complex patterns and nonlinear relationships that signal fraud. Manual processes, while thorough, are not equipped to handle the vast and intricate datasets required to uncover sophisticated fraud schemes, particularly in the B2B and SME sectors.
The problem of limited visibility extends beyond fraud detection. Poor data quality is a widespread concern, with 79% of credit risk executives citing it as a major issue when adopting new risk management frameworks . Missing or incomplete data – especially in less-documented regions or industry segments – can distort risk assessments and place smaller suppliers in underrepresented markets at a disadvantage.
External factors add another layer of unpredictability. Geopolitical and economic upheavals can disrupt a buyer’s business overnight, triggering large insurance losses that standard risk models often fail to anticipate. Insurers also face a unique dilemma: reducing or canceling coverage can push buyers into financial distress, as suppliers may demand advance payments that further strain liquidity.
Operational inefficiencies further complicate these challenges, as discussed below.
Operational Inefficiencies
Manual processes in underwriting and claims management are time-consuming and prone to errors. Traditional methods require extensive analysis of various data sources, slowing down operations and driving up costs. Legacy systems that silo data and rely on human input struggle to handle the sheer volume of information required for modern trade.
The contrast between manual and automated processes is striking. In tasks like completing climate risk questionnaires, AI has cut processing times from over two hours to just 15 minutes – a 90% reduction. Yet many insurers continue to rely on outdated workflows, limiting their ability to scale operations or increase coverage. According to surveys, 75% of senior credit risk professionals point to risk and governance concerns as the main barriers to adopting advanced technologies. As André Düsing explains:
"Traditionally, this process is often complex and time-consuming, requiring the processing of vast amounts of data by humans. AI promises to streamline this process considerably."
These inefficiencies underscore the pressing need for automation and AI in risk management to meet the demands of today’s fast-paced trade environment.
AI-Powered Solutions for Risk Mitigation
Artificial intelligence is reshaping how risk is managed in trade credit insurance. By analyzing vast amounts of data in real time and spotting patterns that traditional methods might miss, AI provides more precise risk evaluations, quicker fraud detection, and faster claims processing. Impressively, 41% of trade credit insurance professionals already use AI in their operations, and a staggering 94% plan to expand its application within the next year.
Improved Creditworthiness Assessments
AI has taken credit assessments to a whole new level. Machine learning models now go beyond traditional financial documents, incorporating unstructured data like news articles, social media sentiment, and expert opinions to create a well-rounded risk profile. With insurers processing tens of thousands of applications daily, AI enables rapid, data-driven decisions. These systems also monitor global data continuously, identifying early warning signs up to 6 to 8 months before major credit events occur – thanks to tools like Moody’s Credit Sentiment Score. Neural networks dig into historical data to uncover subtle patterns and combine them with alternative indicators such as B2B transaction trends, geopolitical changes, and industry-specific risks. Explainable AI (XAI) has further boosted transparency, clearly outlining factors – like declining revenue or unstable industries – that contribute to higher risk ratings. These capabilities not only enhance credit assessments but also strengthen fraud detection efforts.
Fraud Detection Through Pattern Recognition
AI’s ability to identify fraudulent activity is a game-changer. Algorithms compare claims against historical data and external sources, flagging irregularities that manual reviews might overlook. For instance, in controlled tests, the XGBoost model achieved an impressive 87.3% accuracy and an F1 score of 0.86 in identifying insurance fraud. It uses unsupervised methods to catch early outliers. Natural Language Processing (NLP) adds another layer by scanning news, social media, and corporate updates for negative sentiment and early financial health warnings. Machine learning models also analyze trade transactions to detect money laundering, comparing invoice amounts to market rates. Generative AI steps in to monitor parameters like currency, transaction amounts, and timestamps, helping to identify duplicate claims or suspicious shipping routes. For example, it flags unscheduled port stops or shipments that don’t match established business patterns. As highlighted by experts at TCS:
"The way forward for commercial banks lies in proactive fraud risk management… the use of AI powered predictive tools to detect trade fraud is no longer a nice-to-have but an urgent need".
Automated Claims Processing
AI doesn’t stop at risk prediction – it also revolutionizes claims processing, cutting down delays and improving customer experiences. Automation takes over repetitive tasks like data entry and document verification, making the process faster and more efficient. Tools like Optical Character Recognition (OCR) and NLP transform unstructured data – such as handwritten notes, invoices, and financial reports – into structured formats for quick analysis. Automated systems cross-check claims data with internal records and external sources in real time, ensuring accuracy and consistency before payouts are approved. Multi-layer predictive models further enhance this process by spotting anomalies, such as reused images or mismatched dates. These advancements lead to quicker settlements and happier customers. By eliminating bottlenecks and speeding up payouts, AI-driven claims processing not only improves operational efficiency but also strengthens underwriting practices and opens doors for growth.
Implementing AI in Trade Credit Insurance
Using AI in trade credit insurance builds on its existing strengths by focusing on data quality, solid infrastructure, and well-prepared teams. To make this work, businesses need to start with a strong data governance framework.
Data Strategy and Governance
Good AI starts with good data. Before rolling out AI systems, companies must ensure their data is clean, organized, and standardized across various jurisdictions and reporting formats.
Governance plays a key role here. As Daniel de Burca, Head of Policy and Regulatory Affairs at ICISA, points out:
"Governance cannot just be a list that is checked now and then and shoved in a drawer until the next review – it must shape how AI is built, deployed, and monitored in practice throughout the lifecycle of AI use cases".
This means assigning clear accountability for AI risks, rigorously validating data sources to spot any geographic gaps or biases, and setting up regular human reviews. When AI results don’t align with expected market patterns, teams need defined processes for stepping in. Addressing data bias early is also critical – models that lean too heavily on negative signals or unfairly penalize emerging-market buyers can lead to distorted risk evaluations.
Building the Right Technology Infrastructure
AI adoption needs a scalable and flexible technology base. This includes cloud platforms, data lakes, and interconnected systems that let AI pull data directly from existing sources. The infrastructure must handle real-time data processing, moving beyond static quarterly reports to dynamic inputs like daily bank transactions.
Starting small is a smart approach. For instance, using Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to standardize financial statements can save time and validate the system during initial implementation. Modular architecture further speeds things up by separating user experience, business logic, and infrastructure. This method can cut deployment times by 30% to 50% while reusing existing components.
The first focus should be on repetitive, high-volume tasks like data collection and automated underwriting. For example, Atradius processes around 20,000 credit applications daily, combining traditional methods with AI-enhanced systems.
Training Teams for AI Adoption
Technology alone isn’t enough – teams must also be ready to work with AI. Upskilling existing employees in the trade credit insurance sector is often more effective than hiring new talent. Training should highlight how AI complements human expertise, taking over data-heavy tasks so people can focus on strategic thinking and client relationships.
It’s also essential to teach teams how to interpret AI decisions and understand its limitations. Explainable AI (XAI) is a valuable tool here, helping staff grasp the logic behind risk ratings and fostering trust with regulators and clients. As Carter Hoffman, Research Associate at Trade Finance Global, explains:
"AI isn’t here to replace underwriters. It’s here to work alongside them, elevating what they do best".
Clear oversight protocols are a must, ensuring humans can step in when AI outputs don’t match market conditions. Tools like natural language interfaces make it easier for teams to interact with AI systems without needing advanced technical knowledge. By framing AI as a way to remove tedious tasks, companies can help employees focus on higher-value, strategic work.
These steps don’t just improve efficiency – they also strengthen risk management across trade credit insurance.
Compliance and Ethical AI Use
Integrating AI into trade credit insurance introduces powerful tools but also demands strict adherence to regulatory and ethical standards. These systems handle sensitive financial data and make decisions that can significantly impact businesses throughout the supply chain. To navigate this landscape, providers must ensure their AI technology complies with legal requirements while prioritizing fairness and transparency.
Data Privacy and Security
Trade credit insurers must align their AI operations with established frameworks like the European Insurance and Occupational Pensions Authority (EIOPA) Opinion on AI Governance and Risk Management. Issued in August 2025, this framework clarifies how existing regulations, such as Solvency II and the Insurance Distribution Directive, apply to AI systems. These guidelines emphasize conducting risk-based impact assessments to evaluate factors like data processing scale, sensitivity, and the autonomy of AI systems.
Ensuring compliance involves documenting every step of AI decision-making. This not only prepares insurers for regulatory reviews but also fortifies their systems against cyber threats. Additionally, aligning AI operations with the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) is essential for maintaining consistent performance and cybersecurity.
The reliance on third-party data providers adds another layer of complexity. Trade credit insurance hinges on external data, so insurers must ensure these vendors meet the same ethical and governance standards applied internally. This includes validating the origins of data to address potential biases, such as geographic gaps or an overemphasis on negative signals that could distort risk assessments. By implementing these rigorous measures, insurers can balance the drive for innovation with the demands of regulation.
Balancing Innovation with Regulation
Secure data practices provide the foundation for insurers to innovate while staying compliant with regulatory standards. The idea isn’t to view regulation as a barrier but as an opportunity to align innovation with governance. This approach enables growth even as regulatory oversight becomes more stringent.
Governance should be seen as a strategic advantage. Daniel de Burca, Head of Policy and Regulatory Affairs at ICISA, puts it this way:
"The TCI and Surety sector can use regulatory frameworks as a map to success in AI deployment rather than a compliance hurdle before they get on with the real work of innovation."
In the business-to-business (B2B) context, explainability is crucial. Many counterparties, such as MSMEs and sole traders, are considered vulnerable entities. Insurers must move away from opaque decision-making processes that leave clients in the dark. Instead, they should communicate clearly, offering defined timelines and understandable reasons for credit denials. As de Burca notes:
"Communication that demystifies AI decisions rather than hiding behind a black box – ‘Computer says no’ – strengthens trust in the insurer-policyholder relationship."
To ensure accountability, insurers should establish clear triggers for human intervention when AI outputs deviate from expectations. This "human-in-the-loop" approach allows AI to handle high-volume tasks while maintaining oversight. Ethical AI practices not only enhance trust but also reinforce effective risk management in trade credit insurance.
Conclusion
AI is reshaping trade credit insurance by moving from reactive measures to proactive risk management. It identifies early warning signs of potential credit issues as much as 6–8 months in advance. This capability, paired with instant underwriting and automated fraud detection, strengthens the safety net for businesses operating in unpredictable markets.
The momentum is clear: 94% of trade credit insurance professionals plan to expand their AI usage within the next year. Leading players like Atradius are already leveraging AI on a massive scale, processing around 20,000 credit applications daily through AI-powered systems.
Stan Chang, Director Group Buyer Underwriting at Atradius, highlights the transformative potential of AI:
"The holy grail of machine decisioning is to deliver consistent outcomes that produce lower claims (through superior predictive capability), higher premium revenue (from a higher acceptance rate), lower operating costs (via more automatic decisions), and increased customer satisfaction."
The operational advantages speak for themselves: quicker credit decisions, stronger fraud protection, and precise, real-time risk analysis. By integrating AI into underwriting, businesses can scale efficiently while reserving human expertise for more complex, strategic tasks.
To fully unlock AI’s potential, companies need robust data strategies, workforce training, and governance frameworks implemented early in the process. These steps ensure AI doesn’t just enhance trade credit insurance but transforms it into a strategic advantage.
At Accounts Receivable Insurance, we utilize AI-driven innovation to craft trade credit insurance solutions that safeguard your business and support financial security in today’s ever-changing market.
FAQs
What data does AI use to assess buyer risk?
AI assesses buyer risk by analyzing a wide range of information, such as financial metrics, geopolitical events, market trends, real-time financial updates, and recent patterns in financial behavior. These insights improve evaluations of creditworthiness and help detect potential fraud, ultimately lowering risks in trade credit insurance.
How do insurers prevent AI bias in credit decisions?
Insurers are tackling AI bias in credit decisions with a mix of strategies aimed at promoting fairness and accuracy. They start by conducting pre-processing audits to identify potential biases in the data. Techniques like re-weighting and proxy sanitization help refine the data further, ensuring it doesn’t unintentionally favor or disadvantage specific groups. Additionally, they implement fairness-constrained optimization to balance predictive accuracy with equitable outcomes.
On the other side, post-processing methods come into play. These include groupwise calibration and threshold adjustments, which fine-tune the AI’s outputs to minimize uneven impacts. Insurers also rely on multi-metric fairness checks to evaluate models from several angles and incorporate human review of edge cases to catch and address scenarios that automated systems might overlook. Together, these steps work to create credit assessments that are not only accurate but also fair for everyone.
When should a human override an AI underwriting or claims decision?
Human intervention should step in when decisions require fairness, compliance, or nuanced judgment that AI cannot fully grasp. While AI plays a valuable role in improving risk assessments and detecting fraud in trade credit insurance, it’s essential to have human oversight for situations involving ethical considerations, regulatory requirements, or substantial financial and reputational stakes. If AI outputs show signs of bias, inconsistency, or conflict with established facts, human judgment ensures decisions stay fair, accurate, and accountable.



