When choosing between multi-buyer and single-buyer risk policies, the key is understanding how each fits your business needs:
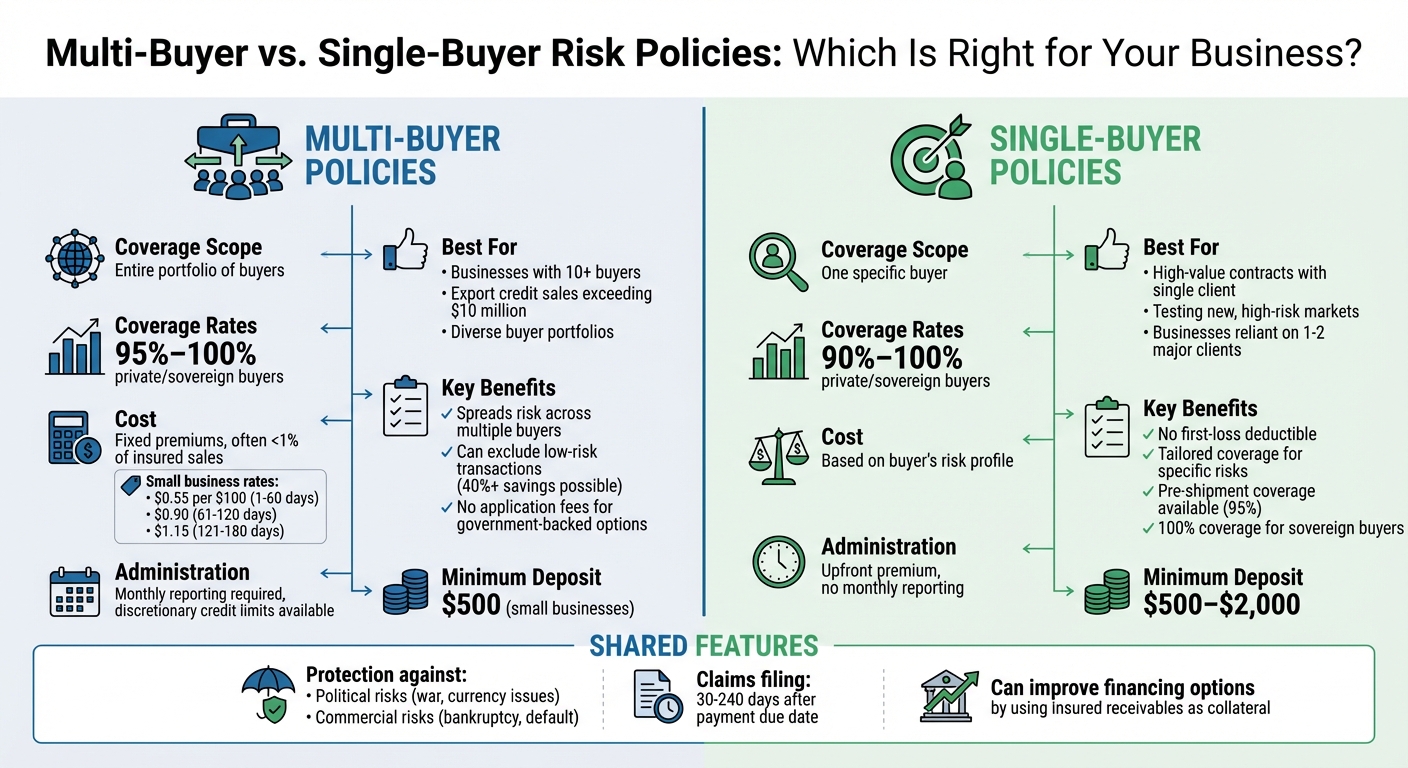
- Multi-Buyer Policies: Cover an entire portfolio of buyers, offering broad protection for businesses with diverse clients. Ideal for exporters managing multiple international customers. Includes features like discretionary credit limits, high coverage rates (up to 95% for private buyers, 100% for sovereign buyers), and cost-effective premiums (often under 1% of insured sales). Best suited for businesses with export credit sales exceeding $10 million or those dealing with more than 10 buyers.
- Single-Buyer Policies: Focus on one specific buyer, providing targeted coverage for businesses reliant on high-value contracts or exploring new markets. Offers up to 90% coverage for private buyers and 100% for sovereign buyers. Suitable for mitigating risks tied to a single client or testing high-risk markets. Requires approval of the buyer’s creditworthiness, and premiums are calculated based on the buyer’s risk profile.
Both policies help mitigate nonpayment risks due to political or commercial issues, like buyer bankruptcy or political unrest, and can improve financing options by using insured receivables as collateral. The choice depends on whether you need broad portfolio coverage or focused protection for specific transactions.
Quick Comparison:
| Feature | Multi-Buyer Policies | Single-Buyer Policies |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage Scope | Entire portfolio of buyers | One specific buyer |
| Coverage Rates | 95%-100% (private/sovereign buyers) | 90%-100% (private/sovereign buyers) |
| Cost | Fixed premiums, often <1% of insured sales | Based on buyer’s risk profile |
| Administration | Monthly reporting, discretionary credit limits | Upfront premium, no monthly reporting |
| Best For | Businesses with diverse buyer portfolios | High-value contracts or new market testing |
The decision ultimately depends on your trade volume, risk tolerance, and whether you need broad or focused coverage.
Multi-Buyer vs Single-Buyer Risk Policies Comparison Chart
Multi-Buyer Risk Policies Explained
What Are Multi-Buyer Risk Policies?
A multi-buyer risk policy is designed to cover an entire portfolio of buyers, whether they are international or domestic, rather than focusing on just one customer. This type of policy provides broad coverage for all foreign receivables, safeguarding exporters against nonpayment caused by political events like war, revolution, or currency issues, as well as commercial risks such as bankruptcy or prolonged defaults.
One key feature of these policies is the inclusion of Discretionary Credit Limits (DCL). This allows experienced exporters to extend credit to buyers up to a pre-approved limit without needing the insurer’s approval for every transaction. This flexibility accelerates the process and reduces administrative hurdles. Additionally, exporters can assign policy proceeds to financial institutions, effectively using insured receivables as collateral. This approach not only enhances liquidity but also broadens borrowing capabilities. Overall, multi-buyer policies simplify risk management for businesses dealing with multiple buyers.
Benefits of Multi-Buyer Policies
Multi-buyer policies offer several practical advantages for exporters. Coverage rates are typically high, with 95% coverage for private sector buyers and 100% coverage for sovereign buyers. For bulk agricultural commodity exports, coverage can go up to 98%.
The cost savings are another standout feature. On average, these policies cost less than 1% of the total insured sales. For small businesses, the rates are particularly competitive: $0.55 per $100 for payment terms of 1–60 days, $0.90 for 61–120 days, and $1.15 for 121–180 days. For example, one small business reduced its premium costs by over 40% by opting for a Select Risk policy, which excluded low-risk buyers. Standard multi-buyer policies often come with portfolio-specific rates, offering discounts for low-risk buyer concentrations or higher volumes of buyers.
Another major benefit is administrative ease. Instead of juggling separate policies for individual customers, exporters can operate under a single, streamlined framework. Many small business multi-buyer policies come with no first-loss deductible. Government-backed options are particularly appealing, as they typically don’t require application fees or annual minimum premiums. Instead, they only ask for a one-time refundable advance deposit starting at $500.
When to Use a Multi-Buyer Policy
A multi-buyer policy is ideal for exporters who sell to multiple international customers and want broad protection without the hassle of managing individual policies. If your business deals with more than 10 buyers and has export credit sales exceeding $10 million, this type of coverage is a logical choice.
For portfolios with mixed risk profiles, the Multi-Buyer Select Risk (MBSR) option is a great fit. To qualify, at least 50% of your total eligible export credit sales must typically be insured under the policy. This option allows you to exclude low-risk transactions – such as sales to Canada, large multinational corporations, or "prime" customers with a solid payment history of at least three years – so you only pay premiums for higher-risk buyers or markets. Even standard policies often exclude certain transactions, like sales to Canada, invoices under $10,000, or those backed by letters of credit.
Eligibility generally requires at least three years of business operations and one year of export credit experience. Claims for nonpayment are typically filed between 90 and 240 days after the payment due date. For private insurers, minimum annual premiums usually range from $15,000 to $20,000, depending on the specific product.
Single-Buyer Risk Policies Explained
What Are Single-Buyer Risk Policies?
Single-buyer risk policies are a specialized type of political risk insurance designed to protect exporters involved in high-stakes transactions with specific foreign buyers. These policies provide coverage against both commercial risks, like buyer bankruptcy, and political risks, such as war, revolution, or restrictions on currency conversion.
For exporters, pre-shipment coverage is particularly valuable. It safeguards manufacturing costs if political events prevent the shipment of goods. Typically, exporters must insure all eligible shipments to the buyer named in the policy unless they receive a waiver. Unlike multi-buyer policies, which cover an entire portfolio of buyers, single-buyer policies focus exclusively on one buyer, offering a more tailored approach.
Benefits of Single-Buyer Policies
Single-buyer policies are designed to provide focused and flexible coverage. They offer reimbursement rates of up to 90% for private buyers and 100% for sovereign buyers. For exporters dealing in bulk agricultural commodities, coverage can go as high as 98%.
One notable advantage is the absence of application fees or annual minimum premiums for exporter-based policies. Instead, EXIM Bank requires a one-time refundable deposit – $500 for small businesses and up to $2,000 for larger companies. Financial Institution Buyer Credit policies have slightly different costs, with minimum premiums starting at $750 for sovereign buyers and reaching $2,500 for private non-financial institutions.
Another key benefit is the lack of a first-loss deductible. This means the insurer covers losses from the very first dollar up to the agreed coverage percentage. Exporters can also opt to pay their premiums upfront based on projected shipment volumes, eliminating the need for monthly reporting.
When to Use a Single-Buyer Policy
Single-buyer policies shine in situations where a business relies heavily on one or two major clients, making it essential to mitigate concentrated financial risk. These policies are particularly useful for high-value contracts where a single buyer default could significantly impact financial stability. Compared to multi-buyer policies, which require insuring all eligible shipments, single-buyer coverage offers a more cost-efficient solution for exporters focusing on specific customers.
This type of policy is also ideal for businesses entering new, high-risk markets. By insuring transactions with a particular customer, exporters can test the waters before committing to broader coverage. It also allows companies to offer competitive open account credit terms to select foreign buyers without extending coverage to their entire client base. For government buyers, single-buyer policies are especially attractive due to the 100% coverage rate.
Claims under these policies can generally be filed between 30 and 150 days after the payment due date, depending on the policy type. Additionally, documented interest on late payments may be covered for up to 180 days after the due date. These policies are accessible to exporters of all sizes, from small businesses to large corporations, with approval contingent on a review of the foreign buyer’s creditworthiness.
Multi-Buyer vs. Single-Buyer Policies
Coverage Scope Differences
The main distinction between multi-buyer and single-buyer policies lies in the breadth of protection they offer for your export business. Multi-buyer policies are designed to cover a broad range of international sales – often requiring at least 50% of your eligible export credit sales to be included. By spreading coverage across multiple buyers, these policies help diversify risk.
On the other hand, single-buyer policies focus solely on transactions with one specific foreign customer. The coverage percentages vary between the two: multi-buyer policies typically provide 95% coverage for private sector buyers, while single-buyer policies generally offer 90% coverage.
Single-buyer policies require insurers to review and approve the specific buyer in advance. Meanwhile, Multi-Buyer Select Risk (MBSR) policies let exporters exclude lower-risk transactions – such as sales to Canada, transactions backed by letters of credit, or deals with long-standing trusted partners – allowing exporters to concentrate on higher-risk areas.
Cost and Administration Comparison
The differences in coverage also lead to variations in how these policies are managed and priced. Multi-buyer policies generally involve monthly shipment reporting and premium payments based on actual sales volumes. In contrast, single-buyer policies often allow for upfront premium payments based on projected sales, eliminating the need for ongoing reporting. This can simplify administration, especially for businesses managing a single large contract.
When it comes to costs, EXIM multi-buyer policies for small businesses use fixed premium rates, regardless of the buyer’s location. For instance, the rates are $0.55 per $100 for payment terms of 1–60 days, $0.90 per $100 for 61–120 days, and $1.15 per $100 for 121–180 days. Single-buyer premiums, however, are calculated based on the specific buyer’s risk profile. Both types of policies often require a refundable advance deposit, typically $500 for small businesses. For larger companies, single-buyer policies may require deposits as high as $2,000.
Multi-Buyer Select Risk policies can lower premiums by excluding lower-risk transactions. Additionally, multi-buyer policies often include a first-loss deductible, meaning the policyholder absorbs initial losses before coverage kicks in. Single-buyer policies, however, usually lack a deductible, providing coverage from the very first dollar of loss.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Here’s a quick comparison of the key benefits and trade-offs between multi-buyer and single-buyer policies:
| Feature | Multi-Buyer Policy Advantages | Multi-Buyer Policy Disadvantages | Single-Buyer Policy Advantages | Single-Buyer Policy Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Higher coverage (95% for private buyers) | Must cover at least 50% of eligible sales | No first-loss deductible | Lower coverage (90% for private buyers) |
| Management | Discretionary credit limits allow for quicker decisions | Requires monthly shipment reporting | Upfront premium payment; no monthly reporting | Each buyer requires prior approval |
| Flexibility | Spreads risk across multiple buyers and markets | Limited flexibility to exclude specific sales | Tailored to insure high-risk customers | Limited to one buyer per policy |
| Cost Efficiency | Can exclude low-risk transactions to lower premiums | May cover sales beyond immediate needs | Focused coverage for specific risks | No discretionary authority for quick approvals |
| Pre-shipment Coverage | Not typically included | N/A | Available (usually 95%) to safeguard manufacturing costs | Only applies to one buyer relationship |
This comparison highlights the strengths and limitations of each policy type, helping exporters choose the one that best aligns with their business needs and risk tolerance.
sbb-itb-2d170b0
How Accounts Receivable Insurance Can Help
Customized Policy Design
When it comes to Accounts Receivable Insurance (ARI), there’s no such thing as a one-size-fits-all solution. Policies are tailored to fit your specific needs, whether that’s based on trade routes, buyer profiles, or the stability of the markets you operate in. For instance, if your business serves a wide range of international customers, a "Whole Turnover Cover" policy might be the best fit, covering multiple buyers. On the other hand, if your focus is on a few key accounts, a "Selected Risk" single-buyer policy can help you manage costs effectively.
Brokers play a key role here, comparing buyer coverage commitments and terms from leading insurers. This ensures you’re not tied to a single insurer’s terms and can align your policy with your financial goals – whether you’re looking to secure better borrowing terms or expand into less stable markets.
"The trade credit insurer will always investigate your particular circumstances and wishes. The result is a tailor made policy at a corresponding affordable premium."
– ICISA
For exporters with a solid track record, the MBSR (Multi-Buyer Selective Risk) option can help reduce premiums by excluding low-risk transactions. Take the example of a small business selling industrial equipment to over 80 countries. By excluding large, well-established multinationals and trusted partners from coverage, they managed to cut their premium costs by over 40%.
These customized policies work hand in hand with proactive risk monitoring and efficient claims management, creating a seamless safety net for your business.
Risk Assessments and Claims Management
ARI doesn’t just stop at providing coverage – it actively monitors your buyers’ creditworthiness to identify potential risks. Tools like Discretionary Credit Limits (DCL) make the process even smoother by granting pre-approved credit limits. This means you can extend credit to buyers without waiting for insurer approval, which is particularly useful for experienced exporters handling large international orders.
If a claim does arise, insurers follow standard waiting periods – typically between 90 and 240 days after a buyer defaults – before processing payouts. Multi-buyer policies generally cover up to 95% of commercial and political risks, while single-buyer policies offer around 90% coverage for private sector buyers. Some policies also eliminate underwriting or collection fees, simplifying the administrative process even further.
"Built-in discretionary authority allows exporters to extend credit terms without prior EXIM approval."
– Export-Import Bank of the United States
Beyond risk protection, ARI can also strengthen your financial position. Policy proceeds can be used as collateral, increasing your borrowing power. For example, a logistics company with $135 million in total sales (including $45 million from exports) used an FCIA Non-Cancelable Limits Policy to address long repayment terms. This allowed their bank to include international sales in the borrowing base, resulting in better financing terms.
Domestic and International Market Coverage
ARI doesn’t just protect your international ventures – it also covers domestic markets. Providers like FCIA offer single-buyer policies that safeguard both U.S. and international buyers, reducing the risk of over-reliance on a few key accounts.
For global operations, multi-buyer policies protect your entire portfolio, while single-buyer policies can be customized for high-value foreign accounts. Both options cover a broad range of risks, including commercial risks like insolvency and extended defaults, as well as political risks such as currency restrictions, war, or civil unrest. And with the cost of trade credit insurance typically amounting to just a fraction of 1% of company sales, it’s an affordable way to manage these risks.
To make things even easier, ARI providers offer online access to real-time policy data. This transparency allows you to make informed credit decisions, whether you’re shipping to U.S. customers or navigating challenging international markets.
What is Trade Credit Insurance? | Credit Insurance explained in 5 minutes
Conclusion
Deciding between multi-buyer and single-buyer risk policies ultimately comes down to what fits your business best. Multi-buyer policies work well for exporters managing diverse international portfolios, while single-buyer policies are ideal for focusing on specific high-value accounts or testing new markets. The analysis above provides detailed coverage figures to guide your decision.
Key factors to consider include buyer volume, risk tolerance, and administrative preferences. For example, multi-buyer policies, like Select Risk, can lower premiums by over 40% by excluding low-risk transactions. On the other hand, single-buyer policies allow you to focus on critical accounts or new ventures without committing to full portfolio coverage.
To make the decision easier, ARI offers tailored solutions that align with your trade routes, buyer profiles, and market conditions. Whether you need Whole Turnover Cover for broad protection or Selected Risk coverage for specific accounts, ARI’s experienced brokers can help you compare options and find the best fit. They also offer valuable extras like comprehensive risk assessments, discretionary credit limits, and the ability to use policy proceeds as collateral – practical tools for managing both domestic and international risks.
Both types of policies provide flexible, cost-effective protection, with premiums often staying under 1% of sales. With ARI’s expertise and customized tools, you can align your policy structure seamlessly with your business operations.
FAQs
What is the difference between multi-buyer and single-buyer risk policies?
Exporters have two main options when it comes to protecting their sales: multi-buyer risk policies and single-buyer policies. Each serves a distinct purpose, offering different levels of coverage, cost structures, and flexibility.
Multi-buyer policies cover an exporter’s entire portfolio of buyers, spreading the risk across multiple accounts. These policies are generally more affordable, with premiums typically costing less than 1% of insured sales. They also allow exporters to exclude low-risk transactions to keep premiums lower and often include a deductible. This makes them a great choice for businesses with a wide range of customers.
On the other hand, single-buyer policies focus on protecting sales to one specific customer. These policies are ideal for companies that depend heavily on a single buyer. However, because they concentrate on one account, premiums are higher, and they don’t usually include deductibles or application fees.
To sum it up, multi-buyer policies are a cost-efficient way to cover multiple accounts, while single-buyer policies offer focused protection for businesses that rely on a key customer.
What are the benefits of multi-buyer policies for managing international customer portfolios?
Multi-buyer policies give businesses the ability to insure an entire portfolio of international customers instead of focusing on just one. This approach spreads risks – like non-payment or political upheaval – across multiple accounts, lessening the financial blow if one buyer defaults.
By insuring a wider customer base, companies can maintain steadier cash flow and often enjoy premium rates that are typically under 1% of insured sales. These policies also offer flexibility, allowing businesses to exclude low-risk transactions, prioritize higher-risk buyers or markets, and make quicker credit decisions without needing prior approval. For U.S. exporters, this means improved liquidity, better risk management, and a stronger position in the global marketplace.
When is a single-buyer risk policy the right choice for a business?
A single-buyer risk policy is a great choice for businesses that rely heavily on a specific customer or contract, especially when operating in international markets. This type of policy offers protection against financial setbacks caused by non-payment, political instability, or bankruptcy tied to that particular buyer.
It’s especially helpful if your business plans to offer credit terms to a key customer but wants to maintain steady cash flow and safeguard against unforeseen risks. This kind of focused coverage is particularly beneficial for companies handling large, high-value transactions with individual buyers.



